Air Monitoring
Technology is Key to the Future of Local Air Quality Monitoring
Oct 07 2013
While politicians debate the future of local air quality management, Air Monitors (UK) MD Jim Mills points to the opportunities presented by new technologies. Jim explains how many of the monitoring objectives, including cost reduction, can be met by deploying the latest developments in instrument, data management and communications technologies. As a result, it is now possible to reduce both the capital and operational costs of monitoring, whilst improving data capture rates and both the quality and availability of data.
The value of data is highest when it is new, so with the benefit of the latest cloud-based data management and communications technologies, it is now possible to view data in near real-time. This brings a number of important additional benefits because the creation of a live communication pathway provides air quality management professionals with the ability to continually assess instrument status, and thereby to implement proactive service regimes that avoid costly emergency call-outs.
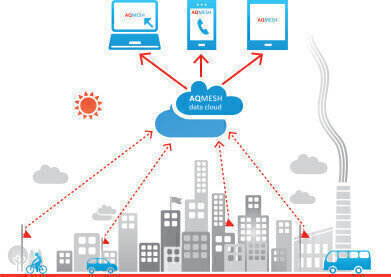
The cost of new monitoring sites need not be preclusive as new technology makes it possible to monitor more locations at a fraction of the cost of traditional stations. In the past, measurement data has been supplemented by modelling but this can lead to significant inaccuracies. The launch of AQMesh is therefore enormously significant; by dramatically lowering the capital and operational costs of monitoring, these new low-cost monitors measure air quality at the point of use – in the street, outside the shop, next to the bus station, by the school…anywhere.
Similarly, a new particulate monitoring technology, FIDAS (Fine Dust Analysis System), runs on low power and without air conditioning and uses no consumables; all of which combine to lower running costs. FIDAS provides continuous real-time simultaneous mass concentration measurements of TSP, PM1, PM2.5 and PM10.
In many cases, there may be no funds for new equipment, so local authorities are naturally looking to extend the working lives of their existing equipment. It is important therefore, for service companies to stock manufacturers’ spares and consumables, and to employ staff with high levels of experience.
In summary, it is extremely worrying that 60 years after the Great Smog of London, thousands are still dying prematurely as a direct result of air pollution. Effective air quality monitoring is therefore essential if we are to tackle this problem, and the current debate should focus on how best to take advantage of the opportunities that new technologies present.
Clearly, less monitoring would lower costs, but so would the introduction of new technologies and practices, without reducing our commitment to address the health problems resulting from air pollution.
Digital Edition
IET 34.2 March 2024
April 2024
Gas Detection - Biogas batch fermentation system for laboratory use with automatic gas analysis in real time Water/Wastewater - Upcycling sensors for sustainable nature management - Prist...
View all digital editions
Events
May 03 2024 Seoul, South Korea
May 05 2024 Seville, Spain
May 06 2024 Minneapolis, MN, USA
May 13 2024 Munich, Germany
May 15 2024 Lund, Sweden