-
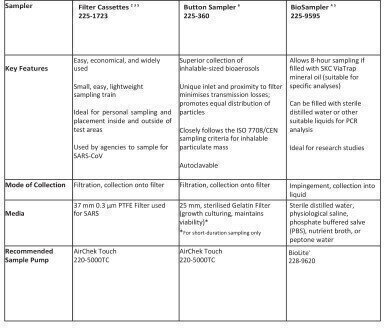 Table 1: Air sampling options for viruses.
Table 1: Air sampling options for viruses. -
 AirChek Touch.
AirChek Touch. -
 BioSampler.
BioSampler. -
 Button Sampler.
Button Sampler.
Laboratory Products
Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) Facts and Sampling Solutions
Apr 03 2020
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines coronavirus (CoV) as a large family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV).
The current occurrence of a new strain known as SARS-CoV-2 (not previously identified in humans) causes coronavirus disease 2019 or COVID-19. On March 11, 2020, WHO publicly characterised COVID-19 as a pandemic.
The Department of Health & Social Care (DHSC) and Public Health England (PHE) are leading the UK government response to the Coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak.
How COVID-19 Spreads
The virus that causes COVID-19 is spread mainly from person-to-person and between people who are in close contact with one another (within approximately 2m). Respiratory droplets are released in an infected person’s coughs/sneezes, similar to influenza. It may be possible for a person to contract COVID-19 by touching a surface or object that has the virus on it andthen touching their own mouth, nose, and/or eyes.
For more detailed information from the Health & Safety Executive (HSE) and the American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA) click here:
Symptoms
These range from mild to severe respiratory illness with fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Some people infected with the virus have reported experiencing non-respiratory symptoms. Other people, referred to as asymptomatic cases, have experienced no symptoms at all. Complications, such as pneumonia in both lungs, can arise and lead to death, particularly in the elderly, immunocompromised/immunosuppressed, or in those individuals who have underlying health conditions.
Symptoms may appear in as few as two days or as long as 14 days after exposure.
Potential Risk
Risk is dependent on exposure. Some people will have increased risk of infection such as workers caring for COVID-19 patients and others in close contact with such patients.
Evaluating COVID-19 in Air
SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19 is a new virus with many unanswered questions. However, scientific professionals can look to previous investigations of corona viruses such as SARS-CoV and the general principles of evaluating biological contaminants. SARS-CoV investigations focused on identifying environmental contamination in infected areas and the potential for transmission to adjacent areas.
Sampling approaches included swab sampling of surfaces and air sampling followed by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)1 analysis.
Listed are some air sampling options for viruses and important details on sampler selection.
Viruses are challenging to culture because they require a host cell to grow.
SKC recommends that you seek guidance from a qualified environmental microbiology laboratory with expertise in viruses before performing any air sampling or studies.
Table 1 shows air sampling options for viruses.
For more information and details of references 1-6 click here
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.2 April 2024
April 2024
In This Edition Chromatography Articles - Approaches to troubleshooting an SPE method for the analysis of oligonucleotides (pt i) - High-precision liquid flow processes demand full fluidic c...
View all digital editions
Events
Apr 28 2024 Montreal, Quebec, Canada
May 05 2024 Seville, Spain
InformEx Zone at CPhl North America
May 07 2024 Pennsylvania, PA, USA
May 14 2024 Oklahoma City, OK, USA
May 15 2024 Birmingham, UK

.jpg)